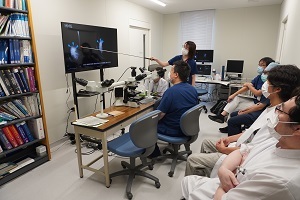
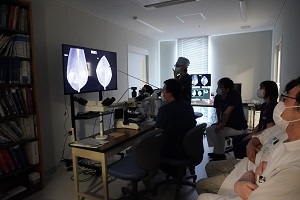
皮膚病理カンファはじめました

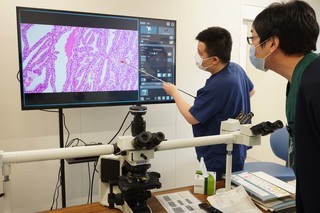
このたび、皮膚科の岡田先生と橘とで、皮膚病理診断カンファレンスをはじめました。病理標本の所見から、組織学的鑑別診断を導き出し、そのあとに臨床情報を聞いて、最終診断を導きだすという、全く新しいアプローチ方法でのカンファレンスです。形成外科の先生方も、奮ってご参加ください。
Dr. Okada from the Department of Dermatology, and Dr. Tachibana from the Department of Diagnostic Pathology, have recently launched a new dermatopathology diagnostic conference. This conference takes a completely novel approach: we begin by formulating a histological differential diagnosis based solely on pathological findings, and then incorporate clinical information to arrive at the final diagnosis.
We warmly invite all plastic surgeons to join us for this unique and educational experience.
-
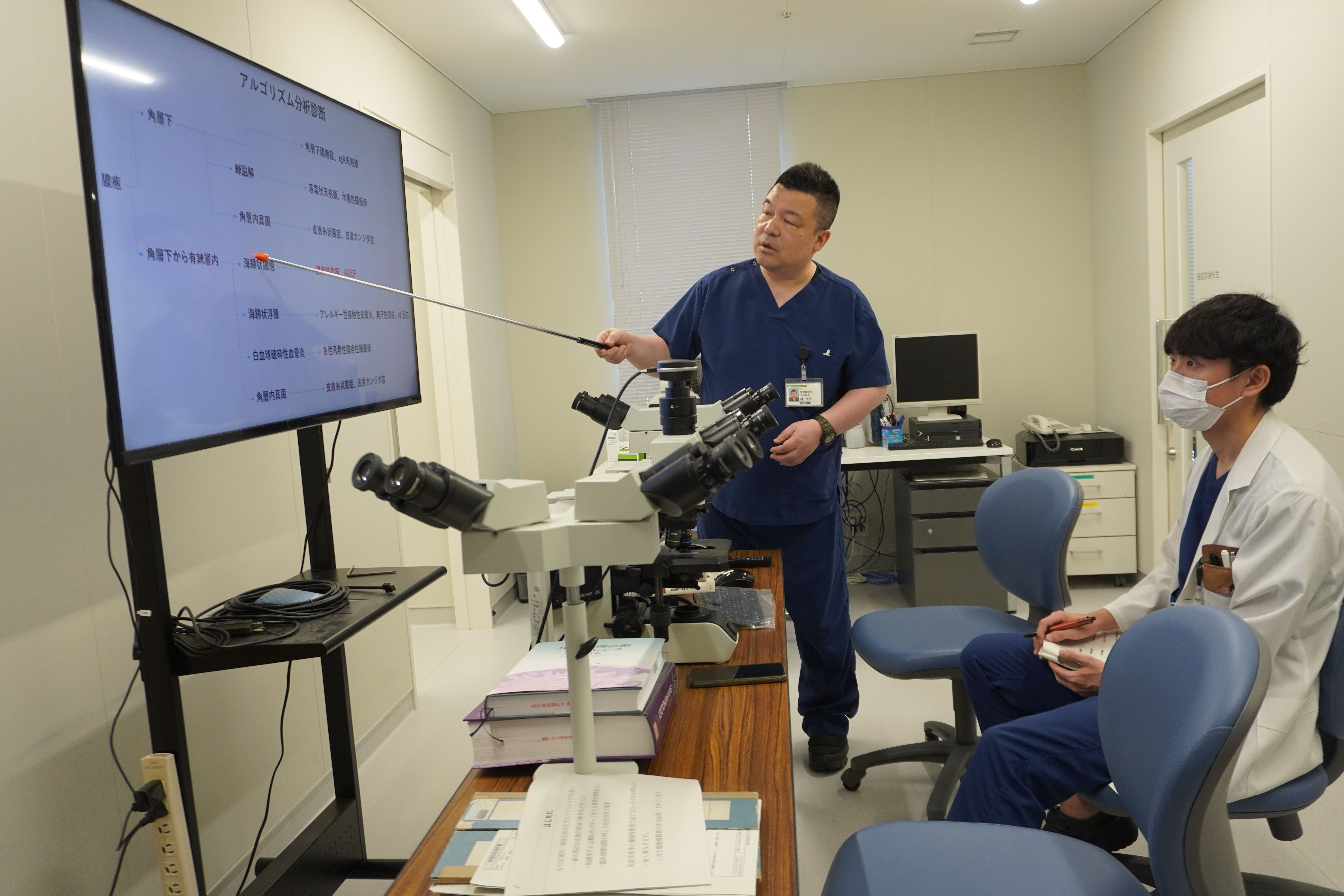

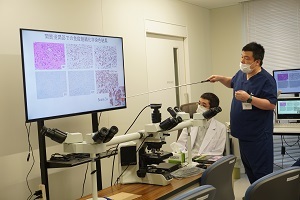
橘医師による説明(1)
-
橘医師による説明(2)
-

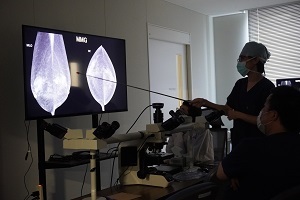
岡田医師による説明(1)
-

岡田医師による説明(2)
医師紹介
| 職名 | 氏名 | 医師免取得年 | 学会専門医資格等 | 備考 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主任部長 | 橘 充弘 | 1999 | 日本病理学会/日本専門医機構認定病理専門医・研修指導医 日本臨床細胞学会認定細胞診専門医・指導医 日本病理学会分子病理専門医 日本病理学会学術評議員 死体解剖資格 医学博士 京都大学医学部附属病院臨床研修指導医のためのワークショップ修了 |
京都大学医学部臨床教授 高知大学医学部客員教授 |
| 非常勤 | 續木 定智 |
2017 |
日本病理学会/日本専門医機構認定病理専門医 日本臨床細胞学会認定細胞診専門医 死体解剖資格 |
藤田医科大学医学部 病理診断学講座 病院助教 |
| 非常勤 | 濱保 英樹 | 2007 | 日本病理学会/日本専門医機構認定病理専門医・研修指導医 日本病理学会学術評議員 日本法医学会認定 法医認定医 日本小児科学会/日本専門医機構認定小児科専門医 死体解剖資格 産業医選任資格 医学博士 |
東京都立小児総合医療センター 病理診断科 |
| 非常勤 | 小杉 伊三夫 | 1985 | 日本病理学会/日本専門医機構認定病理専門医 死体解剖資格 医学博士 |
前・浜松医科大学 再生・感染病理学講座 准教授 |
| 非常勤 | 三浦 克敏 | 1980 | 日本病理学会/日本専門医機構認定病理専門医 日本臨床細胞学会認定細胞診専門医 死体解剖資格 医学博士 |
元・浜松医科大学 基礎看護学(健康科学) 講座 教授 |
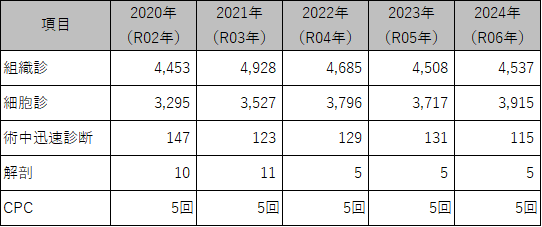
統計
■病理統計
業績
新体制でスタートしました
当院病理診断科には、常勤の病理診断医1名、非常勤病理医師5名と、臨床検査技師7名(うち細胞検査士5名)が所属し、皆様の適切な治療のために病理診断を行っています。
The Department of Diagnostic Pathology has one full-time pathologist, (Mitsuhiro Tachibana, M.D., Ph.D.,), four part-time pathologists (Sadatoshi Tsuzsuki, M.D., Hideki Hamayasu, M.D.,Ph.D., Isao Kosugi, M.D.,Ph.D., and Katsutoshi Miura, M.D.,Ph.D., ), and seven clinical technologists (including five cytologists; CTs) who perform pathological diagnosis for the appropriate treatment of patients.
主任部長の橘充弘医師が京都大学医学部附属病院臨床研修指導医のためのワークショップを修了しました

このたび、橘 充弘医師が第36回京都大学医学部附属病院臨床研修指導医のためのワークショップを修了しました。
主任部長の橘充弘医師が高知大学医学部病理学講座の客員教授に就任しました
このたび、橘 充弘医師が、高知大学教授会より、客員教授の名称を付与されました。
今後とも、橘医師は京都大学医学部・高知大学医学部の学生教育に貢献する所存です。
Dr. Mitsuhiro Tachibana, the Department Head, has been appointed as a Visiting Professor in the Department of Pathology at Kochi University.
The Faculty Council of Kochi University has granted Dr. Tachibana the title of Visiting Professor. Moving forward, Dr. Tachibana will continue to contribute to the education of students at both Kyoto University School of Medicine and Kochi University School of Medicine.
主任部長の橘医師が分子病理専門医に認定されました
このたび、橘主任部長が、2024年度施行第5回分子病理専門医試験に合格し、日本病理学会分子病理専門医として認定されました。
We are pleased to announce that Chief Director Tachibana has passed the 2024 5th Special Molecular Pathologist Examination and has been certified as a Special Molecular Pathologist by the Japan Society of Pathology.
日本専門医機構認定病理専門医資格を更新しました
このたび、主任部長の橘 充弘医師が、病理専門医資格を更新し、専門医に認定されました。
今後も、精度の高い病理診断業務を目指して参ります。よろしくお願いします。
Dr. Mitsuhiro Tachibana, our Chief Director, has successfully renewed his certification as a Pathology Specialist through the Japan Medical Specialty Board. He has been re-recognized as a specialist. Moving forward, we will continue to strive for high-precision pathological diagnostic services. Thank you for your continued support.
放射線画像・病理組織診断カンファレンス

日常業務の中で、興味深い放射線画像を示した症例や珍しい病理組織診断症例について、放射線画像と病理組織画像を照らし合わせて考察するカンファレンスです。
2週間に1回の頻度で開催しております。多数の他業種の方々の参加を推奨します。
We hold a conference every two weeks to discuss interesting cases of radiological images and rare pathological diagnoses. Participants will examine radiological images alongside pathological specimens for insightful analysis. We encourage attendance from professionals across various fields.
-

放射線診断科医師による説明
-
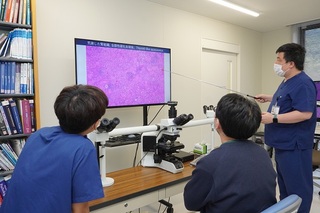
橘医師による説明(1)
-
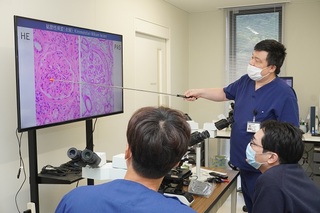
橘医師による説明(2)
-
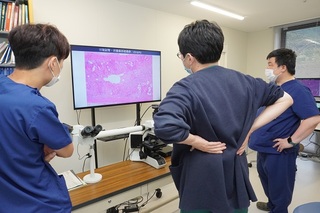
放射線診断科とのディスカッション
乳癌キャンサー・ボード

2024年4月より、乳癌をテーマとした、外科・放射線診断科・放射線治療科・病理診断科合同カンファレンスを月一回のペースで開催しております。検査技師、研修医、看護師の皆様、挙ってご参加ください。
Starting in April 2024, we will hold a monthly interdisciplinary conference on breast cancer involving the departments of Surgery, Diagnostic Radiology, Radiation Oncology, and Diagnostic Pathology. We encourage all medical technologists, residents, and nursing staff to participate actively.
病理診断学について
適切な治療のためには、病気を正しく診断することが前提です。正しく診断するために、主治医は血液検査や放射線画像検査などのいろいろな検査を行います。それらの検査の中に病変部の組織や細胞を採取する検査があり、採取された組織や細胞を顕微鏡で観察して病気を診断するのが病理検査です。つまり、組織や細胞の形態から病気を判断するのが病理診断です。
病理組織標本は固定(人から離れた細胞、組織は徐々に壊れてしまうので、それを防ぐためにホルマリンあるいはエタノールという固定液に入れます)、包埋(薄く切るために、パラフィンとよばれるロウの中に入れて固めます)、薄切[ガラスの上に貼り付けるために3~4マイクロメーター(1000分の1ミリメーター)程度に薄く切ります]、染色(細胞に色をつけて見やすくします)という過程を経て作られます。通常、内視鏡などで採られた小さな組織は1、2日で、手術で切除された胃などの大きな組織は1週間程度で標本となり診断されます。
顕微鏡によって詳しく観察すれば、その組織・細胞の性格は十分判断出来ます。
しかし、中には判断の難しい症例もあります。この場合は通常の染色に加えて、免疫組織化学染色、電子顕微鏡による検鏡などの検索も追加し、さらに日本病理学会や国立がんセンターCIS病理診断コンサルテーション・サービスを利用して他の病理専門医のセカンドオピニオンを得ることによって正しい診断に至るべく努力しています。
また、手術中に切除した臓器の辺縁部に癌が及んでいるか否か、リンパ節などの他の部位へ癌が転移していないかなどを、凍結標本を作ることによって手術中に迅速に診断し、通常10~15分程で手術室へ診断結果を報告します。この病理診断科の迅速診断によって、執刀医は安心して手術を進めることができます。迅速診断の結果によって適切な手術手技が決定されます。
手術で摘出された臓器も病理診断科で検査されます。術前の臨床診断を病理形態的に再確認すると共に、悪いところが完全に取られており、取り残しがないかどうか、リンパ節に転移がないかどうかなども病理診断医が調べます。手術材料の病理診断が出て、初めてその後の治療計画が策定可能になるといっても過言でありません。
残念ながら治療の効なく不幸にして患者さんが亡くなられた場合には、主治医が病理解剖(剖検) の許可をお願いすることがあります。剖検も病理診断科の大切な仕事です。剖検とは、「どうしてこういう症状がでたのか?」とか、「どうして患者さんは亡くならねばならなかったのか?」とか、「治療効果は十分あったのか、治療法は正しかったのか?」などの疑問に対して、病理形態学的解析によって回答することです。どんなに画像診断や特殊な診断技術が向上しても、実際に身体を隅々まで調べることは出来ません。剖検によって初めて確かめられる事実はまだまだ多くあります。もちろん剖検したからといって亡くなられた患者は戻らないのですが、剖検によって明らかになった事実が主治医の貴重な経験となり、よりよい医療に結び付きます。つまり、剖検はその病院の医療の質を保証する大変重要な業務なのです。
当院病理診断科には、常勤の病理診断医1名、非常勤病理医師5名と、臨床検査技師7名(うち細胞検査士5名)が所属し、皆様の適切な治療のために病理診断を行っています。
About Pathological Diagnosis
Correct diagnosis of a disease is a prerequisite for appropriate treatment. In order to make a correct diagnosis, the attending physician performs various tests such as blood tests and radiological imaging examinations. Pathological examinations are performed to diagnose the disease by observing the collected tissues and cells under a microscope. In other words, pathological diagnosis is to determine the disease from the morphology of the tissues and cells.
Histopathological specimens are fixed (cells and tissues that have left the body are placed in a fixing solution called formalin or ethanol to prevent gradual breakdown), embedded (placed in wax called paraffin to make thin slices and harden), and thinly sliced (3 to 4), thin sectioning (cutting into slices as thin as 3 to 4 micrometers (1/1000th of a millimeter) in order to stick them on glass), and staining (coloring the cells to make them easier to see). Usually, a small piece of tissue taken by endoscopy is ready in one or two days, and a large piece of tissue removed by surgery, such as from the stomach, is ready in about one week.
Detailed observation under a microscope is sufficient to determine the nature of the tissue and cells.
However, some cases are difficult to determine. In such cases, in addition to the usual staining, we also use immunohistochemical staining, electron microscopy, and other techniques to obtain a second opinion from other pathologists through the Japanese Society of Pathology and/or the National Cancer Center CIS Pathology Diagnosis Consultation Service in order to reach a correct diagnosis. In addition, we are making efforts to reach a correct diagnosis by obtaining second opinions from other pathologists through the Japanese Society of Pathology and/or the National Cancer Center CIS Pathology Consultation Service.
In addition, we can quickly diagnose during surgery whether or not the cancer has spread to the margins of the removed organ or to other sites such as lymph nodes by preparing frozen specimens and report the results to the operating room within 10 to 15 minutes. This rapid diagnosis by the pathology department allows the primary surgeon to proceed with the surgery with peace of mind. The results of the rapid diagnosis determine the appropriate surgical procedure.
Organs removed during surgery are also examined by the pathology department. In addition to reconfirming the preoperative clinical diagnosis in terms of intraoperative consultation, the pathologist also examines whether or not the bad parts have been completely removed, whether or not any parts remain undone, and whether or not there are any metastases in the lymph nodes, especially sentinel lymph nodes of the breast cancer. It is no exaggeration to say that only after the pathological diagnosis of the surgical material is made can a treatment plan be formulated.
In the unfortunate event that a patient dies after an ineffective treatment, the attending physician may request permission for a pathological autopsy (autopsy). Autopsies are also an important part of the work of the Department of Diagnostic Pathology. An autopsy is an examination of a patient's condition to determine "Why did the patient have these symptoms? or "Why did the patient have to die? and "Was the treatment effective and correct? and "Was the treatment effective and was it correct? No matter how much imaging and special diagnostic techniques are improved, it is not possible to actually examine every inch of the body. There are still many facts that can only be confirmed by autopsy. Of course, an autopsy does not bring back a deceased patient, but the facts revealed by an autopsy provide valuable experience to the attending physician and lead to better medical care. In other words, autopsy is an especially important operation that guarantees the quality of medical care at a hospital.
The Department of Diagnostic Pathology has one full-time pathologist, (Mitsuhiro Tachibana, M.D., Ph.D.,), five part-time pathologists (Akihiko Sugimoto, M.D., Hideki Hamayasu, M.D.,Ph.D., Isao Kosugi, M.D.,Ph.D., Katsutoshi Miura, M.D.,Ph.D., and Yutaka Tsutsumi, M.D.,Ph.D.,), and seven clinical technologists (including five cytologists; CTs) who perform pathological diagnosis for the appropriate treatment of patients.
優秀演題賞を受賞しました

令和5年6月11日に名古屋市にて開催されました、第64回日本臨床細胞学会総会春期大会にて、
示説ポスターセッションで、主任部長の橘 充弘医師が発表しました。
演題名:膵液吸引細胞診で印環細胞様細胞が出現し腸型膵管内乳頭粘液性癌と確定診断し得た1例。
厳正な審査の結果、この度、優秀演題賞を受賞しました。
賞状と記念品(となりのトトロのマグカップ) が贈呈されました。
-

優秀演題賞 賞状
-

記念品のマグカップ
病理診断科活動報告
1)泌尿器科・放射線科・病理診断科合同カンファレンス; キャンサー・ボード
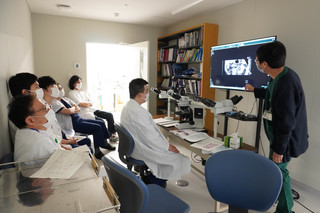
当科では、隔週水曜日午前8:30 から、約30分程度、泌尿器科症例(通常2例)に関して、キャンサー・ボードカンファレンスを行っております。泌尿器科医師・研修医・放射線診断科医師・放射線治療科医師・病理診断科医師が参加し、臨床所見・放射線画像所見・病理組織学的所見を、電子カルテとdiscussion 顕微鏡に直結した、4K大型モニターで、症例提示・discussion を行っております。
他科医師の参加・研修医の積極的な参加も推奨しております。

The Department holds a Cancer Board Conference every other Wednesday morning at 8:30 a.m. for about 30 minutes for urological cases (usually two cases).
Urologists, residents, diagnostic radiologists, radiotherapists, and diagnostic pathologists participate in the conference and present and discuss clinical, radiological, and histopathological findings on a large 4K monitor directly connected to an electronic medical record and a discussion microscope.
We encourage the participation of physicians from other departments and residents.
2)放射線診断科・病理診断科合同カンファレンス

当科では、隔週木曜日午前8:30 から、約30分程度、全科の症例(通常2例)に関して、放射線画像診断・細胞診・組織診断についてカンファレンスを行っております。
放射線診断科医師病理診断科医師が参加し、臨床所見・放射線画像所見・細胞診所見・病理組織学的所見を、電子カルテとdiscussion 顕微鏡に直結した、4K大型モニターで、症例提示・discussion を行っております。
他科医師の参加・研修医の積極的な参加も推奨しております。
Every other Thursday at 8:30 a.m., we hold a 30-minute conference on radiological imaging, cytology, and histopathology for all departments' cases (usually two cases).
The radiologists and pathologists attend the conference and present and discuss clinical, radiological, cytological, and histopathological findings on a large 4K monitor directly connected to the electronic medical record and the discussion microscope.
We encourage the participation of physicians from other departments and residents.
-
病理医による説明風景
-
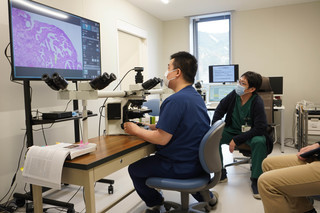
病理医による説明風景
-

Discussion 風景
研究の情報公開文書
すべて新規ウィンドウで開きます。
※現在、情報公開文書はありません。
研修について
文責:病理診断科